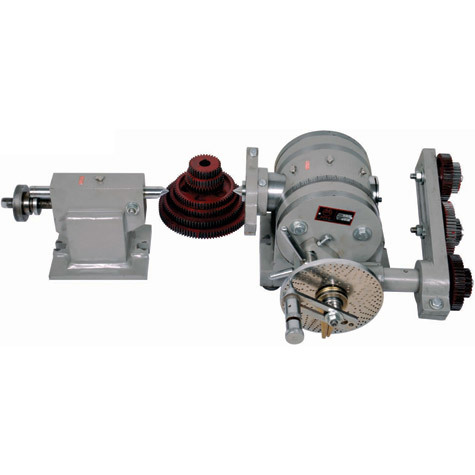
Dividing Head
Product Details:
- Dimension (L*W*H) 180X115X180 Millimeter (mm)
- Weight (kg) 40 Kilograms (kg)
- Warranty 6 MONTH
- Click to view more
Dividing Head Price And Quantity
- 10
- 37100.00 INR/Piece
Dividing Head Product Specifications
- 6 MONTH
- 180X115X180 Millimeter (mm)
- 40 Kilograms (kg)
Dividing Head Trade Information
- Cheque Telegraphic Transfer (T/T)
- 1 Week
- Yes
- Within a certain price range free samples are available
- All India
Product Description
-
Rotational Capability: Dividing heads are designed to rotate the workpiece or tool at precise angles, typically in degrees or minutes, and can rotate both clockwise and counterclockwise. This feature is crucial for performing operations like cutting gears, fluting, and indexing holes.
-
Indexing: Dividing heads have indexing mechanisms that allow the operator to set specific divisions or angles for machining. These divisions are typically marked on a dividing plate, and a handle or crank is used to engage the indexing mechanism. The indexing plate has holes or notches at regular intervals to facilitate accurate angular positioning.
-
Compatibility: Dividing heads can be attached to various types of machine tools, such as milling machines, grinders, or drill presses. They are versatile tools that can adapt to different machining requirements.
-
Chuck or Collet: Dividing heads often have a chuck or collet that securely holds the workpiece or tool in place while it's being rotated and machined.
-
Precision: One of the primary advantages of using a dividing head is its precision. It allows for highly accurate and repeatable machining operations, making it ideal for tasks like cutting gear teeth, indexing holes, and machining other intricate features.
-
Tailstock: Some dividing heads come with a tailstock that provides additional support to longer workpieces, improving stability during machining.
-
Graduated Scales: Dividing heads often have graduated scales, dials, or vernier scales that make it easy to set specific angles with precision.
Applications of dividing heads include:
-
Gear Cutting: Dividing heads are commonly used for cutting the teeth of gears, as gear teeth need to be evenly spaced around the gear's circumference.
-
Indexing Holes: They are used for drilling or milling holes at precise intervals on a workpiece.
-
Fluting: Dividing heads are used for creating flutes in cylindrical parts, such as end mills and drills.
-
Thread Cutting: Dividing heads can be employed for cutting threads on cylindrical workpieces.
-
Complex Machining: They are used when a part requires multiple machining operations at specific angles or divisions.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese